Strokes: Warning Signs & Brain Function Impacts
What is a Stroke?
A stroke occurs when the blood flow to the cerebral arteries in the brain is disrupted, and some brain cells don’t get the oxygen and nutrients they need. The affected brain cells die and that area of the brain can’t function as it did when they were alive. The American Heart Association/American Stroke Association says that strokes are the #5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the United States.
As shown in the image below, with an Ischemic stroke (left), blood clot stops flow of blood to an area of the brain. With a Hemorrhagic stroke (right), blood leaks into brain tissue.
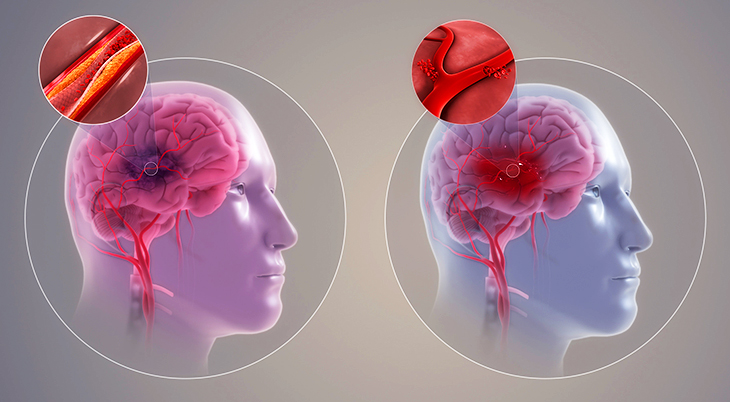 (Ischemic & Hemorrhagic Stroke Images: https://www.scientificanimations.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
(Ischemic & Hemorrhagic Stroke Images: https://www.scientificanimations.com, CC BY-SA 4.0)
How Are People Affected by Stroke?
Left and Right Brain Hemispheres & Brain Functions
The right hemisphere of the brain controls the left side of the body, and the left hemisphere of the brain controls the right side of the body. For these reasons, if a stroke occurs in the right side of the brain, the left side of the body will be affected. Some functions are controlled by both hemispheres of the brain, and other functions are controlled by either the left or right hemisphere, as the infographic below demonstrates.
In summary, depending on which hemisphere of the brain a stroke occurs in, different functions may be impacted as follows:
Left Hemisphere of the Brain
- the right side of the body, ie hand, arm, leg movements
- language – spoken language and written language
- reasoning and analytical skills, including mathematical and scientific functions & calculations
Right Hemisphere of the Brain
- the left side of the body, ie hand, arm, leg movements
- spatial orientation
- artistic functions, creativity, and awareness, including music
- insight
6 Regions of the Brain & Brain Functions
The left and right hemisphere of the brain are divided into 6 regions that each control different functions, as the infographic below demonstrates.
In summary, depending on which region and hemisphere a stroke occurs in, different functions may be affected as follows:
Frontal Region of the Brain
- Personality, behaviour control
- Speaking and writing abilities
- Emotions and arousal
- Intelligence
- Ability to problem solve, plan, make decisions, put things in order, concentrate
- Voluntary movements
Parietal Region of the Brain
- Sensations – pain, touch, temperature and the ability to understand and interpret sensory information – size, colour, shape
- Understanding space and distance
- Mathematical calculations
Occipital Region of the Brain
- Vision and interpreting what is seen
Cerebellum Region of the Brain
- Balance and posture
- Motor coordination (body movement)
- Fine motor skills
Brain Stem Region of the Brain
- Breathing
- Heart rate control
- Consciousness, alertness, wakefulness
- Swallowing
- Blood pressure
- Sweating
Temporal Region of the Brain
- Language skills and abilities
- Hearing
- Memory including long-term
- Organization and planning
- Behaviour and emotions
Warning Signs of Stroke
This video covers what a stroke is, the warning signs (symptoms) to watch out for, what to do in the event of a stroke, and how to reduce the risk of having a stroke.
It’s not just seniors that need to know about strokes.
For more information about strokes, consult your doctor(s) and these resources:
The Heart & Stroke Foundation of Canada
The American Stroke Association
More About Heart Disease, Heart Attacks, High Blood Pressure/Hypertension, And Strokes
Atrial Fibrillation: Risk Factors
Heart Attack Symptoms (men)
Signs of a Heart Attack For Women
Hormone Therapy for Menopause and Heart Disease
High Blood Pressure: Risks, Causes, and Prevention
High Blood Pressure: Fish Oil Supplements
Peripheral Artery Disease: Symptoms & Risk Factors
